Research
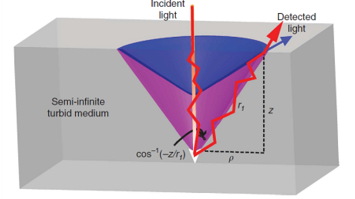
Propagation of Light in Turbid Media
From astronomy to cell biology, the manner in which light propagates in turbid media has been of central importance for many decades. The theory of radiative transfer is widely used to treat this problem by considering
the transport of light energy through a random medium and neglecting the wave properties. The basic equation in transport theory is the equation of transfer, for which analytic solutions cannot be obtained for most
realistic problems...
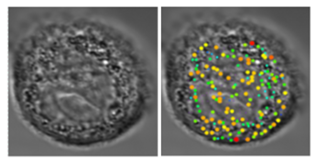
Label-Free Nanoscale-Sensitive Study of Sub-Cellular Morphology
Despite the fact that cancer is a disease caused by genetic abnormalities, the most widely accepted means of diagnosing and characterizing cancer cells is with H&E stained microscopic imaging. The identifying features
of cancer include abnormally large and crowded cell nuclei with altered cellular organization and shape and increased number of nucleoli...

In Vivo Noninvasive Optical Detection of Invisible Precancer in the Human Digestive System
The purpose of this program is to develop optical systems that can perform rapid optical scanning and multispectral imaging of the entire epithelial surface of various organs in the in the human digestive system and present
a diagnosis in near real time...
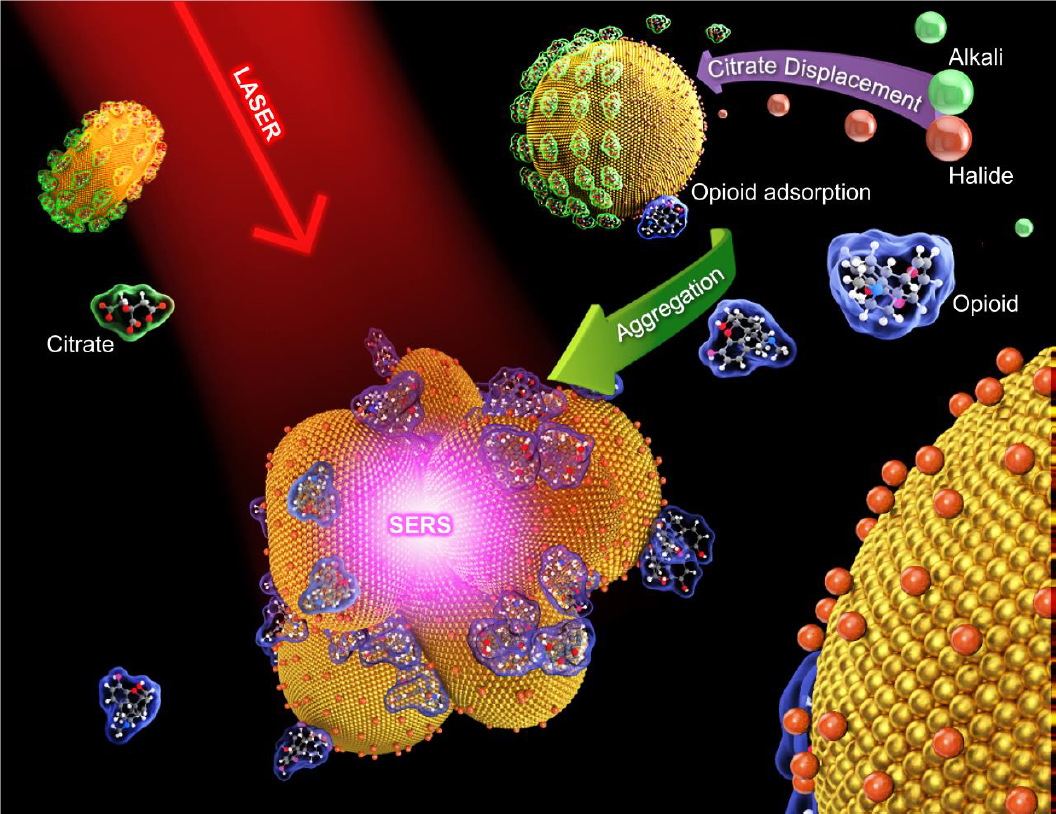
SERS-based Ultrasensitive Identification and Quantification of Drugs in Biofluids
The enormous increase of Raman signal in the vicinity of metal nanoparticles allows surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) to be employed for label-free detection of substances at extremely low concentrations. However,
the ultimate potential of label-free SERS to identify pharmaceutical compounds at low concentrations, especially in relation to biofluid sensing, is far from being fully realized...